- directly (https://peaka.studio/),
- in an Embedded UI (https://docs.peaka.com/how-to-guides/how-to-embed-peaka-to-my-app),
- Use your OAuth implementation, provide tokens to Peaka
- Use Peaka OAuth mechanism
1. Use Your OAuth Implementation
Partners may have an already implemented OAuth process and OAuth apps. In order to use these apps, Peaka needs clientId, clientSecret, refreshToken and accessToken. Since partner makes all OAuth flows, it is sufficient to pass these info to Peaka. This is the simplest integration way of OAuth. Upon getting refresh token and access token from the OAuth Provider (e.g. Google), the Partner will make “create connection” request.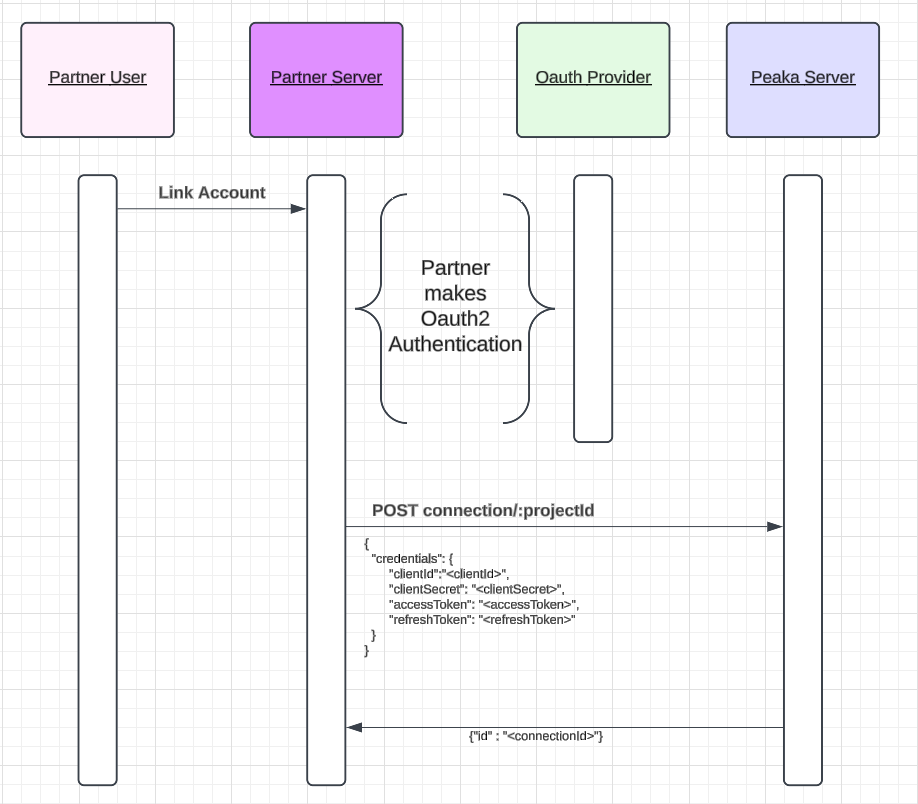 A typical request example will be
A typical request example will be
2. Use Peaka OAuth Mechanism
OAuth flows are a bit complex to implement for some partners. Defining and registering appropriate OAuth apps can also be complex and time consuming (e.g. Some platforms may have longer review process). Peaka does the complex part and informs you when an OAuth flow has completed. Since everything happens in the user browser, such integration is more complex than the previous. Whether you will be using Peaka OAuth App or your own OAuth app, this mechanism can be implemented in two ways:2.a. Use Peaka OAuth App
When you choose to use Peaka OAuth app for some Platform (e.g. Google Analytics), OAuth flow will end at Peaka site and Peaka will inform you after that. Using Peaka OAuth app has some advantages and disadvantages. Also in some cases, you should use your own OAuth app. Advantages:- Some platforms enable public creation of an OAuth app, some requires developer accounts, and some requires a partnership program. Also they may have review process. Peaka has completed review process of the Platform you are using. So you don’t need to wait for your own.
- In OAuth flow, a consent screen will be shown to your user. In that screen, Peaka’s branding and logo will be shown. If you need to show your logo and branding, you should choose to create your own OAuth app and implement the next option.
- Platforms may have strict rate limits. To avoid rate limits, you may consider creating your own oauth app.
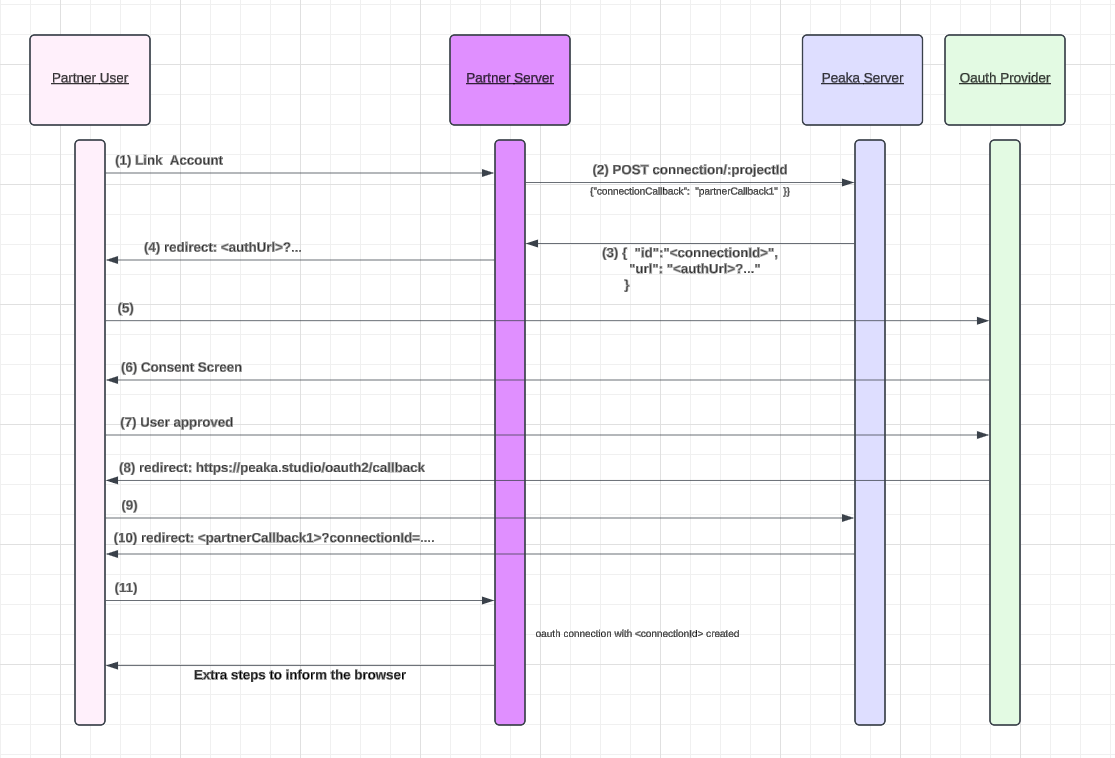
- Your user clicks a button in your application in order to create connection. e.g. Google Analytics connection. The response of this http request will be done in Step 4.
- Your server should make a create connection request
partner_callback_url is the full url of your server endpoint responsible to complete creation process. We will use partner_callback_url at Step 10 and 11.
- As a response to the request in Step 2
- Your server should return redirect:<platform_consent_url> to the browser as response to the request initiated at Step 1. Also it is a good practice to store
connection_idand the location where the user has started the connection.
- Browser will automatically redirect to Platform Consent Screen.
- Browser shows the Consent Screen.
- User will approve the consents.
- Platform will return the Peaka OAuth app’s redirect (oauth2 callback of Peaka) redirect:https://peaka.studio/oauth2/callback
- Browser will be redirected to Peaka Callback.
- Peaka will return a redirection to your
partner_callback_url:
- The browser will be redirected to your
<partner_callback_url>with query parametersconnectionIdandstatus. Ifstatusissuccess, the connection has been created successfully. Otherwise, ifstatusisfail, it indicates a problem, such as a platform error or a timeout in the flow.
2. b. Use Your Own OAuth App
You should create your own app,- if you need to use your own branding and logo
- if you need better rate limits for the Platform API
- if Peaka supports connection for the Platform but does not have a global app.
- Here, global app means that the Platform allows Peaka use data of other users. Sometimes the platforms allow only non-global apps or there are long review processes for the global apps.
- You can use Peaka’s own callback url.
- You can use your own redirect url and then redirect it to the Peaka’s callback.
partner_callback_url
e.g. You give the OAuth app redirect_url as https://yourdomain.com/oauth2/mycallback
Then you should redirect the request coming to your redirect_url to https://peaka.studio/oauth2/callback
You can do this redirection in your reverse proxy server (Apache, Nginx, Traefik, etc.) or in your application server (Express in Node.js, Spring in Java, etc.).
Apache (HTTPD)
- You can use your own callback url and the user’s browser will never redirected to Peaka’s domain.

- Your user clicks a button in your application in order to create connection. e.g. Google Analytics connection. The response of this http request will be done in Step 4.
- Your server should make a create connection request
redirect_url under “credential” object should be the callback (or redirect) url you give to the Platform OAuth app.
- As a response to the request in (2)
- Your server should return redirect:<platform_consent_url> to the browser as response to the request initiated at Step 1. Also it is a good practice to store
connection_idand the location where the user has started the connection.
- Browser will automatically redirect to Platform Consent Screen
- Browser shows the Consent Screen.
- User will approve the consents.
- Platform will return the your OAuth app’s redirect url - you give in Step 2 - with some query parameters.
- Browser will be redirected to your callback with some query parameters.
- A typical
redirect_urlwill be
- Response of Step 10 will be